Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, where data is generated at an unprecedented rate and instant access is a necessity, both edge computing and cloud computing play vital roles in meeting the evolving needs of businesses and individuals. While these two computing paradigms serve distinct purposes, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing is complementary, creating a powerful synergy that optimizes performance, scalability, and data processing capabilities. This article explores the dynamic relationship between edge computing and cloud computing, delving into their integration, advantages, challenges, and real-world applications.
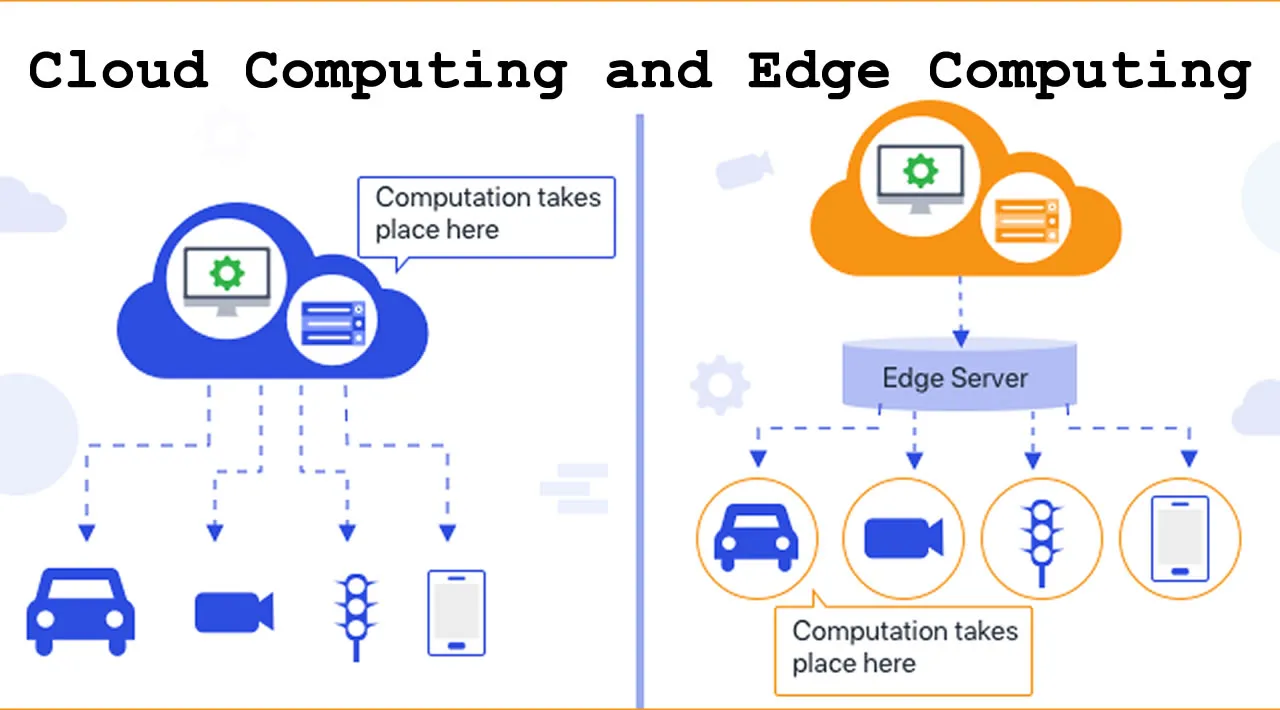
What Is Edge Computing and Cloud Computing?
Before delving into their relationship, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals of edge computing and cloud computing.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing refers to a distributed computing model that brings computational capabilities and data storage closer to the source of data generation. By processing data closer to where it is produced (at the “edge” of the network), edge computing reduces latency, enhances real-time decision-making, and alleviates bandwidth constraints. It empowers devices at the network edge, such as IoT devices, to perform local computations and filter data before transmitting it to the cloud.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing, on the other hand, involves the delivery of computing resources (including storage, processing power, and applications) over the internet. Cloud computing enables organizations and individuals to access shared pools of resources on-demand, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. It centralizes data storage and processing in remote data centers, allowing users to access their data and applications from anywhere, at any time.
Seamless Integration and Advantages
The integration of edge computing with cloud computing brings about numerous advantages that enhance the performance, scalability, and data processing capabilities of both paradigms. Here are some key advantages:
- Latency Reduction: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing significantly reduces latency. Real-time applications, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote healthcare, benefit greatly from reduced latency, as it enables faster decision-making and response times.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, optimizing bandwidth usage. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios with limited connectivity or high costs associated with data transmission.
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing adds an extra layer of redundancy and resilience to the overall system. In the event of network disruptions or intermittent connectivity, edge devices can continue to operate autonomously, ensuring uninterrupted services and operations.
- Scalability: The combination of edge computing and cloud computing allows for dynamic scalability. Edge devices can offload computationally intensive tasks to the cloud, leveraging its vast resources. This elasticity enables seamless scaling to accommodate changing demands, optimizing resource allocation and reducing costs.
- Enhanced Security: Edge computing improves security by reducing the attack surface area. Sensitive data can be processed locally, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access during data transmission. Additionally, edge computing allows for data encryption and anonymization closer to the source, providing an additional layer of protection.
Real-World Use Cases
The integration of edge computing and cloud computing has already proven its worth in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few compelling examples:
- Smart Cities: Edge computing and cloud computing work together to create efficient, sustainable, and interconnected smart cities. Sensors deployed throughout the city collect real-time data on traffic, energy consumption, air quality, and more. Edge devices process and analyze this data locally, enabling timely responses and localized actions. The cloud complements this by aggregating and analyzing data on a larger scale, providing actionable insights for urban planning and resource management.
- Retail and E-commerce: In the retail industry, edge computing enables personalized customer experiences. Edge devices within physical stores collect and analyze data on customer behavior, enabling real-time recommendations and targeted promotions. Cloud computing supports these edge devices by processing large-scale customer data, facilitating inventory management, and optimizing supply chain operations.
- Industrial IoT: Edge computing and cloud computing play critical roles in industrial IoT applications. Edge devices installed on factory floors or oil rigs can monitor equipment health, detect anomalies, and trigger immediate responses. Cloud computing enables advanced analytics, predictive maintenance, and centralized monitoring of multiple edge devices across distributed locations.
Challenges and Considerations
While the integration of edge computing and cloud computing offers significant benefits, it is not without its challenges. Here are a few considerations:
- Data Synchronization: Achieving seamless data synchronization between edge devices and the cloud can be complex, especially in scenarios where intermittent connectivity or network disruptions occur. Implementing efficient synchronization protocols and strategies is crucial to ensure consistency and accuracy of data across the system.
- Security and Privacy: Combining edge computing and cloud computing introduces new security considerations. Protecting data at the edge, during transmission, and within the cloud is paramount. Implementing robust encryption, access controls, and privacy frameworks is essential to safeguard sensitive information.
- Cost Management: While the integration of edge and cloud computing offers cost savings through optimized bandwidth usage and resource allocation, there are additional costs associated with deploying and maintaining edge infrastructure. Organizations must carefully evaluate the trade-offs and determine the most cost-effective approach.
Conclusion
The relationship between edge computing and cloud computing is one of synergy and mutual benefit. By leveraging the strengths of each paradigm, organizations can achieve enhanced performance, scalability, and data processing capabilities. The integration of edge and cloud computing paves the way for exciting advancements in various domains, from smart cities to healthcare, manufacturing, and beyond. As technology continues to evolve, the seamless integration of edge and cloud computing will undoubtedly shape the future of computing, unlocking new possibilities and driving innovation.